NEWS & BLOG

The Role of a Manager: Optimism in the Face of Adversity In the intricate dance of organizational dynamics, the role of a manager is both pivotal and multifaceted. At its core, management involves navigating through change and addressing problems, particularly when outcomes deviate from expectations. Unlike employees focused on their specific tasks, managers must oversee the broader picture, ensuring that every part of the machine runs smoothly. This oversight often means that managers find themselves perpetually in the trenches of negativity—dealing with issues, mitigating crises, and steering teams through turbulent waters. Managing Change and Problem-Solving One of the fundamental responsibilities of a manager is to manage change. Change, whether anticipated or unexpected, is a constant in the business world. Managers are tasked with guiding their teams through transitions, ensuring minimal disruption to productivity and morale. This involves strategic planning, clear communication, and effective implementation of new processes or policies. When things go awry or fail to produce the desired results, it falls upon the manager to step in and rectify the situation. Problem-solving is an inherent part of management. Identifying the root cause of an issue, devising solutions, and implementing corrective actions are all within a manager’s purview. This requires not only technical and industry-specific knowledge but also the ability to think critically and adapt quickly. The Shadow of Negativity Given their role, managers do not spend a significant amount of time on aspects that are functioning well. Instead, their attention is predominantly drawn to areas that require improvement or intervention. This focus on problem areas can create an environment of perpetual negativity, which, if not managed properly, can be detrimental to a manager’s morale and overall effectiveness. The Importance of Optimism In light of the challenges managers face, assessing potential managers for their level of optimism becomes crucial. Optimism, particularly in the face of adversity, is a key trait that can significantly influence a manager’s ability to lead effectively. Optimistic managers are more likely to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than insurmountable obstacles. They can maintain a positive outlook, which can be contagious, inspiring their teams to remain motivated and engaged even during tough times. Coupling Optimism with Critical Thinking and Common Sense While optimism is a valuable trait, it must be balanced with critical thinking and common sense. An effective manager is not blindly positive but rather possesses a realistic optimism grounded in practical wisdom. This balance allows them to remain hopeful and forward-thinking while making sound decisions based on thorough analysis and logical reasoning. Critical thinking enables managers to evaluate situations from multiple perspectives, consider various solutions, and anticipate potential outcomes. Common sense, on the other hand, ensures that their decisions are pragmatic and applicable to the real world. Together, these qualities enable managers to navigate complex situations with both positivity and prudence. Conclusion In conclusion, the role of a manager is inherently challenging, requiring a delicate balance between addressing issues and maintaining team morale. Optimism in the face of adversity is a crucial trait for effective management, providing the resilience and positivity needed to lead teams through difficult times. However, this optimism must be tempered with critical thinking and common sense to ensure that decisions are both hopeful and practical. By evaluating potential managers on these criteria, organizations can ensure they have leaders capable of steering them through the inevitable ups and downs of the business landscape.

The Declining Population of China: Implications for Global Supply Chains and Consumer Prices I China's population has been shrinking since 2022, and the United Nations has predicted that it could drop to 1.3 billion by 2050 and 770 million by 2100. This is due to fewer newborns and more deaths from an aging population. The population is expected to fall by 20 million to 1.39 billion by 2035 Understanding the Decline China, known for having the world’s largest population, is experiencing a decline that could reshape its economic and global trade role. The decline is attributed to several factors, including lower birth rates, aging population, and stringent past policies like the one-child policy. The effects of this demographic change are beginning to ripple across various sectors, particularly impacting manufacturing and the global supply chains that depend heavily on Chinese labor and production capabilities. Impact on Global Supply Chains 1. Increased Production Costs: China has long been the world’s factory, known for its cost-effective labor which has enabled lower production costs globally. However, as the working-age population shrinks, there will likely be a shortage of labor which could drive up labor costs due to the increased competition for workers. Higher labor costs in China could lead to increased manufacturing costs, which might force companies to reassess their production and supply chain strategies. 2. Shifts in Manufacturing Hubs: With rising costs in China, companies might look to diversify their manufacturing locations to other countries with younger populations and lower wage expectations, such as India or Vietnam. This shift could lead to a reconfiguration of supply chain networks, which may result in initial disruptions and increased costs as new systems and infrastructures are put in place. 3. Technological Investment and Automation: To counteract the labor shortage, there might be an accelerated investment in automation and robotics. While this could mitigate the impact of reduced labor availability in the short term, it also requires significant upfront investment and could lead to a greater concentration of technical expertise rather than widespread labor benefits. Effect on Consumer Prices 1. Increase in Product Prices: As production costs rise due to higher labor costs and potential tariffs from diversified supply chains, consumer prices are likely to increase. Products that are heavily dependent on Chinese manufacturing, such as electronics and textiles, could see significant price hikes. 2. Fluctuations in Supply and Demand: A reduced population also means a decrease in domestic consumption within China. For international businesses, this represents a dual challenge: navigating the increase in production costs and adjusting to a potentially reduced Chinese consumer market. However, this could also lead to an excess of goods, which might temporarily lower prices in other markets until supply chains adjust. 3. Global Market Adjustments: The global market will need to adjust to these shifts. Countries and companies that adapt quickly, diversifying their markets and supply sources or investing in automation, will likely fare better. Consumer prices will stabilize over time, but the initial impact could be significant depending on the industry and the speed of demographic changes. Conclusion The declining population in China is a harbinger of significant changes in global supply chains and economic structures. As companies and countries navigate this new demographic landscape, the impacts on production costs, supply chain logistics, and consumer prices will become increasingly apparent. Adapting to these changes will require strategic planning, investment in technology, and diversification of supply and market bases. The global economy is on the brink of a significant transformation, and understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders at all levels.

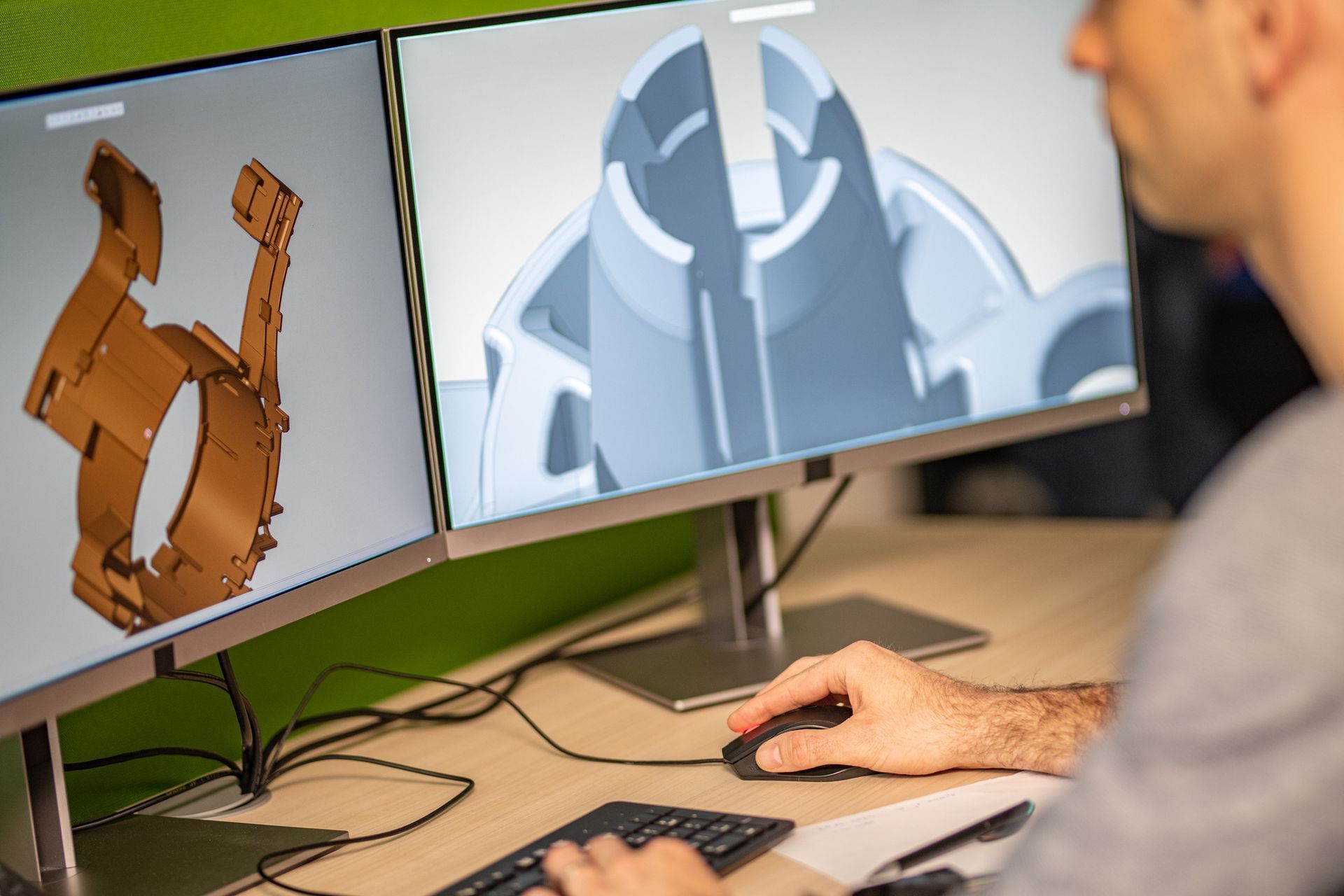
In the ever-evolving competition to differentiate a business and stand out from the crowd while maintaining maximum efficiency, a delicate balance must be struck between standardization and customization. While customers are drawn to unique and personalized experiences, the behind-the-scenes operations of a business often thrive on consistency and efficiency.

In many aspects of business and life, we are encouraged to celebrate achievements and successes. However, there is a growing need to reevaluate our approach when it comes to rewarding mere "shots on goal." Many people think this was caused by the "every kid gets a trophy culture". In this post, we will explore the concept of not rewarding every attempt, why it is important, and how it can foster a culture of excellence and growth.

At ZYCI, we value our AS9100 certification, it has made us a better supplier and put us on a journey of continuous improvement. Perfection is ever elusive, but we will never stop the pursuit.
In today's aerospace industry, quality and reliability are critical factors that cannot be compromised. One way to ensure that you are working with a reliable supplier is to choose one that is AS9100 certified. AS9100 is a quality management system standard that is specifically designed for the aerospace industry. Here are some of the key benefits of doing business with an AS9100 certified supplier:
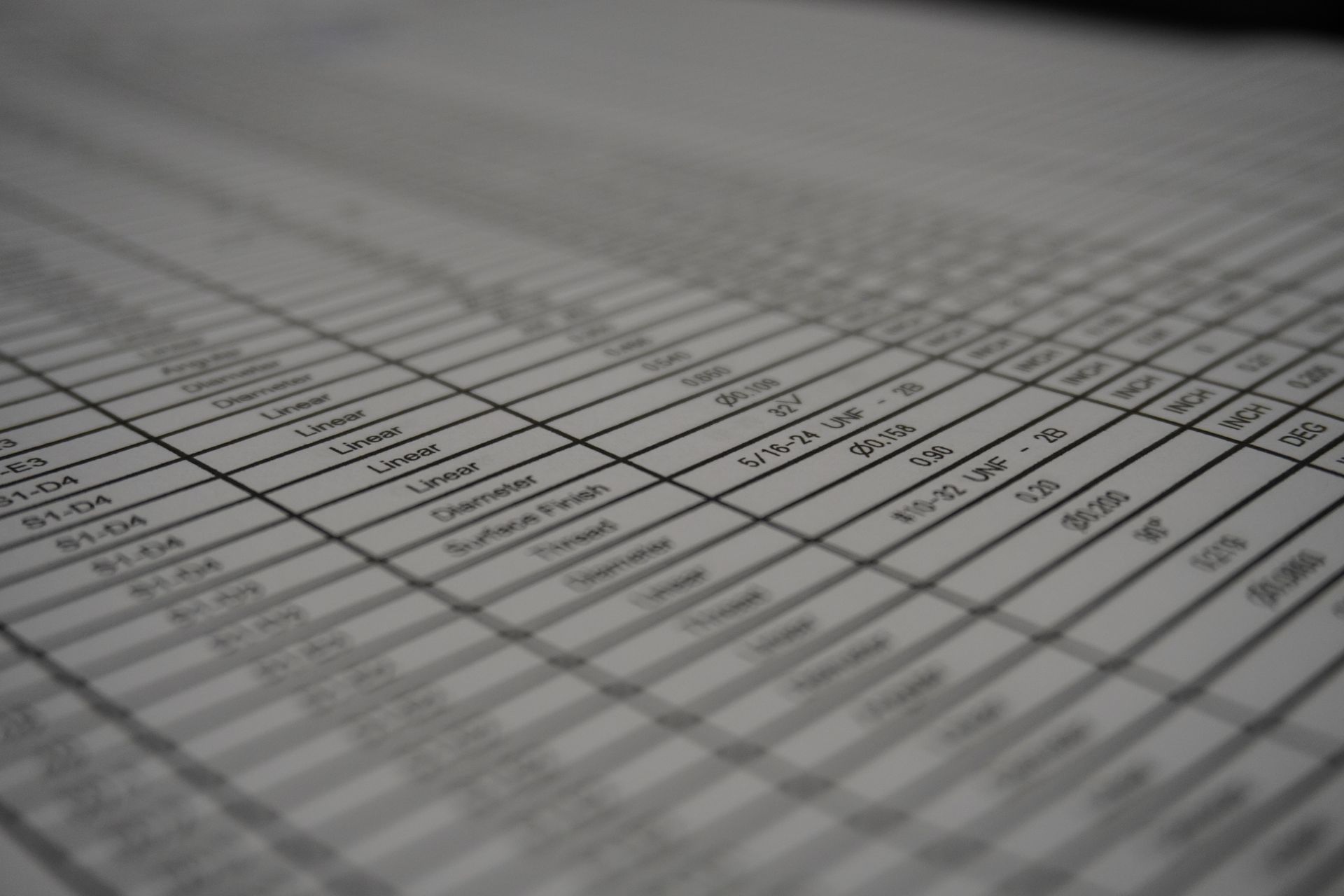
When it comes to precision machined parts, quality documentation plays a crucial role in ensuring all specifications are met and complying with flow downs. If the quality documentation requirements were not clearly articulated with the request for quote (RFQ), we will often ask the customer to confirm their requirements. The documentation and certifications as cost and often lead-time, as such it is important for us to fully understand the requirements up front so the pricing and lead-times quote match the requirements.
Regardless of the documentation level required, we guarantee the parts will be manufactured to the required specifications and tolerances. You just may not need to incur the added cost for formal documentation.

ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) and EAR (Export Administration Regulations) are U.S. government regulations that control the export and import of defense-related articles and services, including certain technical data and software. These regulations are designed to protect national security by restricting the export of sensitive military technologies to foreign countries or foreign nationals who are not authorized to receive them. If a machining project involves the production of parts or components that are considered defense-related or have potential military applications, it may be subject to ITAR or EAR controls. In such cases, the project may require compliance with specific regulatory requirements, including registration with the U.S. State Department or the U.S. Commerce Department, obtaining export licenses, and implementing appropriate security measures to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure of controlled technical data. It is important to ask whether a machining project is ITAR or EAR controlled because non-compliance with these regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and loss of export privileges. Additionally, failure to comply with ITAR or EAR controls can harm national security by potentially facilitating the unauthorized transfer of sensitive technologies to foreign countries or non-authorized parties. When a customer submits a quote request we will often confirm with the customer to be 100% we understand if the project is controlled by ITAR or EAR export regulations. If a project is ITAR or EAR controlled: We store the data on our encrypted drive and handle it in compliance with CMMC and NIST800-171 If we need to get a quote from a finisher, we can't email the drawing to them (we send a link the encrypted file for download) We can't email photos or images to our customer if we have a DFM question If we have visitors that are non-U.S. persons, ensure they do not catch a glimpse of the parts on a tour Inquire about DFARS or domestic material requirements (if that was not made clear in the RFQ) Inquire about quality reports, certifications and CoC's that may be required Make sure we receive a copy of all the flow downs that would come with a purchase order Mitch Free

Metal 3D printing and CNC machining are both important manufacturing technologies that serve different purposes and have their own advantages and disadvantages. While metal 3D printing has gained popularity for its ability to produce complex geometries and one-of-a-kind parts, CNC machining remains a key technology for producing high-precision parts at scale. Metal 3D printing has limitations in terms of speed, size, and cost when compared to CNC machining. CNC machines are typically faster and can produce larger parts with higher accuracy and at a lower cost per unit than metal 3D printers. In addition, CNC machines can work with a wider range of materials than metal 3D printers, including metals that are difficult or impossible to 3D print. However, metal 3D printing is useful for producing parts with complex geometries that cannot be machined easily, such as parts with internal channels, intricate shapes, or undercuts. It also allows for the production of one-off or low-volume parts without the need for expensive tooling. Overall, metal 3D printing and CNC machining are complementary technologies that can work together to achieve different manufacturing goals. While metal 3D printing may replace some CNC machining applications in certain contexts, it is unlikely to make CNC machining obsolete. Today, the general rule of thumb is that if a part can be machined, it should be machined. Otherwise the economics just doesn't make sense. Mitch Free




















